Search This Blog
Tuesday, 28 December 2010
finding N number of most CPU consuming process in Solaris.
Saturday, 25 December 2010
Custom Logrotate in Solaris 10
1. Add the corresponding entries in /etc/logadm.conf in below format.
root@server1 # tail -3 /etc/logadm.conf
/var/adm/wtmpx -A 1m -o adm -g adm -m 664 -p 1d -t '$file.old.%Y%m%d_%H%M' -z 1
/var/adm/wtmpx -A 1m -g adm -m 664 -o adm -p 1w -t '$file.old.%Y%m%d_%H%M' -z 5
/var/adm/utmpx -A 1m -g adm -m 664 -o adm -p 1w -t '$file.old.%Y%m%d_%H%M' -z 5
/var/adm/loginlog -A 1m -g sys -m 700 -o root -p 1w -t '$file.old.%Y%m%d_%H%M' -z 5
Explanation for each switch:
-A ->Delete any versions that have not been modified for the amount of time specified by age. Specify age as a number followed by an h (hours), d (days), w(weeks), m (months), or y (years).
-o -> the owner of the newly creating empty file
-g-> the group of newly creating file
-m ->mode of the new empty file (chmod xxx)
-p -> Rotate a log file after the specified time period (period as d, w, m, y)
-t -> Specify the template to use when renaming log files (Here, wtmpx.old.20101225_0757) (see man logadm for more info)
-z ->How many copy of rotaged files needs to retain on the system.
-P ->Used by logadm to record the last time the log was rotated in /etc/logadm.conf (no need to set this manually)
2. Once above entries are done, execute logadm -v command to run a logrotation now. Now logadm reads the /etc/logadm.conf file, and for every entry found in that file checks the corresponding log file to see if it should be rotated.
root@server1 # logadm -v
# loading /etc/logadm.conf
# processing logname: /var/log/syslog
# using default rotate rules: -s1b -p1w
# using default template: $file.$n
# processing logname: /var/adm/messages
# using default rotate rules: -s1b -p1w
# using default template: $file.$n
# processing logname: /var/cron/log
# using default expire rule: -C10
# processing logname: /var/lp/logs/lpsched
# using default rotate rules: -s1b -p1w
# processing logname: /var/fm/fmd/errlog
# using default expire rule: -C10
# using default template: $file.$n
# processing logname: /var/fm/fmd/fltlog
# using default template: $file.$n
# processing logname: smf_logs
# using default template: $file.$n
# processing logname: /var/adm/pacct
# using default template: $file.$n
# processing logname: /var/log/pool/poold
# using default expire rule: -C10
# using default template: $file.$n
# processing logname: /var/svc/log/system-webconsole:console.log
# using default rotate rules: -s1b -p1w
# using default expire rule: -C10
# using default template: $file.$n
# processing logname: /var/opt/SUNWsasm/log/sasm.log
# using default template: $file.$n
# processing logname: /var/adm/wtmpx
mkdir -p /var/adm # verify directory exists
mv -f /var/adm/wtmpx /var/adm/wtmpx.old.20101225_1250 # rotate log file
touch /var/adm/wtmpx
chown adm:adm /var/adm/wtmpx
chmod 664 /var/adm/wtmpx
# recording rotation date Sat Dec 25 12:50:51 2010 for /var/adm/wtmpx
# processing logname: /var/adm/utmpx
mkdir -p /var/adm # verify directory exists
mv -f /var/adm/utmpx /var/adm/utmpx.old.20101225_1250 # rotate log file
touch /var/adm/utmpx
chown adm:adm /var/adm/utmpx
chmod 664 /var/adm/utmpx
# recording rotation date Sat Dec 25 12:50:51 2010 for /var/adm/utmpx
# processing logname: /var/adm/loginlog
mkdir -p /var/adm # verify directory exists
mv -f /var/adm/loginlog /var/adm/loginlog.old.20101225_1250 # rotate log file
touch /var/adm/loginlog
chown root:sys /var/adm/loginlog
chmod 700 /var/adm/loginlog
# recording rotation date Sat Dec 25 12:50:51 2010 for /var/adm/loginlog
# writing changes to /etc/logadm.conf
As you can see the last line of above command, once the logadm command successfully run, it do some changes to with -P switch in /etc/logadm.conf file regarding the last update of logrotation.
root@server1 # tail -3 /etc/logadm.conf
/var/adm/wtmpx -A 1m -P 'Sat Dec 25 12:50:51 2010' -g adm -m 664 -o adm -p 1w -t '$file.old.%Y%m%d_%H%M' -z 5
/var/adm/utmpx -A 1m -P 'Sat Dec 25 12:50:51 2010' -g adm -m 664 -o adm -p 1w -t '$file.old.%Y%m%d_%H%M' -z 5
/var/adm/loginlog -A 1m -P 'Sat Dec 25 12:50:51 2010' -g sys -m 700 -o root -p 1w -t '$file.old.%Y%m%d_%H%M' -z 5
List of new files created in /var/adm
root@server1 # ls -ltr /var/adm/*.old*
-rwx------ 1 root sys 0 Dec 25 11:00 /var/adm/loginlog.old.20101225_1250
-rw-r--r-- 1 root bin 3720 Dec 25 15:49 /var/adm/utmpx.old.20101225_1250
-rw-rw-r-- 1 adm adm 8595060 Dec 25 15:51 /var/adm/wtmpx.old.20101225_1250
Tuesday, 21 December 2010
Growing Sun Cluster File System with new Disks.
Number of Nodes: 2
Node Name: Node1 and Node2
Cluster: Sun Cluster 3.2
OS: Solaris 9/10
/dev/md/apps-ms/dsk/d300 295G 258G 35G 89% /apps/data
2. Configure all the fiber channels on both nodes with below steps.
root@Node1 # cfgadm -al|grep fc
c4 fc-fabric connected configured unknown
c5 fc connected unconfigured unknown
c6 fc-fabric connected configured unknown
c7 fc connected unconfigured unknown
root@Node1 # cfgadm -c configure c4 c5 c6 c7
root@Node1 #devfsadm –C
(Repeat steps 2 and 3 in all cluster nodes)
4. Run format command to list all the disks, the newly configred disk can be seen at top of format as below (if the disk not labeled already)
root@Node1 # format
Searching for disks...done
c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000104d0: configured with capacity of 99.98GB
c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000120d0: configured with capacity of 99.98GB
s7 ->100mb (this 100 mb is reseverd for metadb creation. Not mandatory)
s0 -> remaining space.
Configuring DID devices
did instance 95 created.
did subpath Node2:/dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000120d0 created for instance 95.
did instance 96 created.
did subpath Node2:/dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000104d0 created for instance 96.
did instance 97 created.
did subpath Node2:/dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000103d0 created for instance 97.
Configuring the /dev/global directory (global devices)
obtaining access to all attached disks
(above command resulted in createing d95, d96, d97 devices)
95 Node2:/dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000120d0 /dev/did/rdsk/d95
95 Node1:/dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000120d0 /dev/did/rdsk/d95
96 Node2:/dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000104d0 /dev/did/rdsk/d96
96 Node1:/dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000104d0 /dev/did/rdsk/d96
97 Node2:/dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000103d0 /dev/did/rdsk/d97
97 Node1:/dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000103d0 /dev/did/rdsk/d97
root@Node2 # metaset -s apps-ms -a /dev/did/rdsk/d95 /dev/did/rdsk/d96 /dev/did/rdsk/d97
root@Node2 # metattach -s apps-ms d300 /dev/did/rdsk/d95s0 /dev/did/rdsk/d96s0 /dev/did/rdsk/d97s0
apps-ms/d300: components are attached
root@Node2 # metastat -s apps-ms -p d300 apps-ms/d300 2 3 d6s0 d7s0 d8s0 -i 32b \
3 d95s0 d96s0 d97s0 -i 32b
/dev/md/apps-ms/rdsk/d300: 1257996288 sectors in 76782 cylinders of 64 tracks, 256 sectors
614256.0MB in 12797 cyl groups (6 c/g, 48.00MB/g, 5824 i/g)
super-block backups (for fsck -F ufs -o b=#) at:
32, 98592, 197152, 295712, 394272, 492832, 591392, 689952, 788512, 887072,
Initializing cylinder groups:
...............................................................................
...............................................................................
...............................................................................
..................
super-block backups for last 10 cylinder groups at:
1257026336, 1257124896, 1257223456, 1257322016, 1257420576, 1257519136,
1257617696, 1257716256, 1257814816, 1257913376,
root@Node2 # df -h|grep d300
/dev/md/apps-ms/dsk/d300 591G 258G 330G 44% /apps/data
Dec 21 10:07:21 Node1 Cluster.devices.did: [ID 287043 daemon.notice] did subpath /dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000120d0s2 created for instance 95.
Dec 21 10:07:22 Node1 Cluster.devices.did: [ID 536626 daemon.notice] did subpath /dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000104d0s2 created for instance 96.
Dec 21 10:07:22 Node1 Cluster.devices.did: [ID 624417 daemon.notice] did subpath /dev/rdsk/c8t6005076305FFC08C0000000000000103d0s2 created for instance 97.
Dec 21 10:07:22 Node1 Cluster.scdpmd: [ID 922726 daemon.notice] The status of device: /dev/did/rdsk/d95s0 is set to MONITORED
Dec 21 10:07:22 Node1 Cluster.scdpmd: [ID 922726 daemon.notice] The status of device: /dev/did/rdsk/d96s0 is set to MONITORED
Dec 21 10:07:22 Node1 Cluster.scdpmd: [ID 489913 daemon.notice] The state of the path to device: /dev/did/rdsk/d96s0 has changed to OK
Dec 21 10:07:22 Node1 Cluster.scdpmd: [ID 489913 daemon.notice] The state of the path to device: /dev/did/rdsk/d95s0 has changed to OK
Dec 21 10:07:22 Node1 Cluster.scdpmd: [ID 922726 daemon.notice] The status of device: /dev/did/rdsk/d97s0 is set to MONITORED
Dec 21 10:07:22 Node1 Cluster.scdpmd: [ID 489913 daemon.notice] The state of the path to device: /dev/did/rdsk/d97s0 has changed to OK
Dec 21 10:07:39 Node1 Cluster.devices.did: [ID 466922 daemon.notice] obtaining access to all attached disks
Network troubleshooting from OBP (OK prompt)
{0} ok watch-net
Timed out waiting for Autonegotiation to complete
Check cable and try again
Link Down
{0} ok watch-net-all
/pci@3,700000/network@0,1 ----------------------> path to interface
Timed out waiting for Autonegotation to complete
Check cable and try again ----------------------> No cable is connected/active
Link Down
Timed out waiting for Autonegotation to complete
Check cable and try again
Link Down
Timed out waiting for Autonegotation to complete
Check cable and try again
Link Down
Timed out waiting for Autonegotation to complete
Check cable and try again
Link Down
/pci@3,700000/network@0 -------------------> path to interface
1000 Mbps full duplex Link up
Looking for Ethernet Packets.
'.' is a Good Packet. 'X' is a Bad Packet.
Type any key to stop.
40 42 42 40 42 42 40 40 42 42 40 1ed 42 42 40 42 40 42 40 42 42 40 42 40 42 40 42 42 40 42 40 42 40 42 42 40 40 42 42 40 40 42 42 40 42 42 40 40 42 42 40 42 42 40 42 40 42 40 42 42 40 42 40 42 40 42 42 40
/pci@2,600000/network@0,1
1000 Mbps full duplex Link up
Looking for Ethernet Packets.
'.' is a Good Packet. 'X' is a Bad Packet.
Type any key to stop.
40 44 44 44 40 7a 40 f7 40 40 40 1ed 40 40
/pci@2,600000/network@0
1000 Mbps full duplex Link up
Looking for Ethernet Packets.
'.' is a Good Packet. 'X' is a Bad Packet.
Type any key to stop.
42 40 42 42 40 42 40 42
/pci@0,600000/pci@0/pci@8/pci@0/network@2,1
Timed out waiting for Autonegotiation to complete
Check cable and try again
Link Down
/pci@0,600000/pci@0/pci@8/pci@0/network@2
Timed out waiting for Autonegotiation to complete
Check cable and try again
Link Down
For getting the details about each interfaces, go to the corresponding path using cd comammnd, and run the properties as below
{0} ok cd /pci@3,700000/network@0
{0} ok .properties
mac-address 00 15 17 3b xx xx
link-clock auto
duplex auto
speed auto
status okay
assigned-addresses 82020010 00000000 00100000 00000000 00020000
82020014 00000000 00120000 00000000 00020000
81020018 00000000 00000300 00000000 00000020
82020030 00000000 00140000 00000000 00020000
phy-type mif
board-model 501-7289
version Sun PCI-E 1G Ethernet UTP Adapter FCode 1.10 06/11/02
model SUNW,pcie-northstar
d-fru-len 00000800
d-fru-off 00006800
d-fru-dev eeprom
s-fru-len 00000800
s-fru-off 00006000
s-fru-dev eeprom
compatible pciex8086,105e.108e.125e.6
pciex8086,105e.108e.125e
pciex108e,125e
pciex8086,105e.6
pciex8086,105e
pciexclass,020000
pciexclass,0200
reg 00020000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
02020010 00000000 00000000 00000000 00020000
02020030 00000000 00000000 00000000 00020000
max-frame-size 00010000
address-bits 00000030
device_type network
name network
local-mac-address 00 15 17 3b xx xx --> MAC Address for /pci@3,700000/network@0
fcode-rom-offset 0000e000
interrupts 00000001
cache-line-size 00000010
class-code 00020000
subsystem-id 0000125e
subsystem-vendor-id 0000108e
revision-id 00000006
device-id 0000105e
vendor-id 00008086
{0} ok cd /pci@2,600000/network@0,1
{0} ok .properties
status okay
assigned-addresses 82020110 00000000 00160000 00000000 00020000
82020114 00000000 00180000 00000000 00020000
81020118 00000000 00000320 00000000 00000020
82020130 00000000 001a0000 00000000 00020000
phy-type mif
board-model 501-7289
version Sun PCI-E 1G Ethernet UTP Adapter FCode 1.10 06/11/02
model SUNW,pcie-northstar
d-fru-len 00000800
d-fru-off 00006800
d-fru-dev eeprom
s-fru-len 00000800
s-fru-off 00006000
s-fru-dev eeprom
compatible pciex8086,105e.108e.125e.6
pciex8086,105e.108e.125e
pciex108e,125e
pciex8086,105e.6
pciex8086,105e
pciexclass,020000
pciexclass,0200
reg 00020100 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
02020110 00000000 00000000 00000000 00020000
02020130 00000000 00000000 00000000 00020000
max-frame-size 00010000
address-bits 00000030
device_type network
name network
local-mac-address 00 15 17 3d xx xx --> MAC Address for /pci@2,600000/network@0,1
fcode-rom-offset 0000e000
interrupts 00000002
cache-line-size 00000010
class-code 00020000
subsystem-id 0000125e
subsystem-vendor-id 0000108e
revision-id 00000006
device-id 0000105e
vendor-id 00008086
{0} ok cd /pci@2,600000/network@0
{0} ok .properties
status okay
assigned-addresses 82020010 00000000 00100000 00000000 00020000
82020014 00000000 00120000 00000000 00020000
81020018 00000000 00000300 00000000 00000020
82020030 00000000 00140000 00000000 00020000
phy-type mif
board-model 501-7289
version Sun PCI-E 1G Ethernet UTP Adapter FCode 1.10 06/11/02
model SUNW,pcie-northstar
d-fru-len 00000800
d-fru-off 00006800
d-fru-dev eeprom
s-fru-len 00000800
s-fru-off 00006000
s-fru-dev eeprom
compatible pciex8086,105e.108e.125e.6
pciex8086,105e.108e.125e
pciex108e,125e
pciex8086,105e.6
pciex8086,105e
pciexclass,020000
pciexclass,0200
reg 00020000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
02020010 00000000 00000000 00000000 00020000
02020030 00000000 00000000 00000000 00020000
max-frame-size 00010000
address-bits 00000030
device_type network
name network
local-mac-address 00 15 17 3d xx xx --> MAC Address for /pci@2,600000/network@0
fcode-rom-offset 0000e000
interrupts 00000001
cache-line-size 00000010
class-code 00020000
subsystem-id 0000125e
subsystem-vendor-id 0000108e
revision-id 00000006
device-id 0000105e
vendor-id 0000808
Tuesday, 26 October 2010
Mounting LVM volume after reinstalling Linux
Today, I reinstalled my Linux box with latest Redhat version, but I failed to mount the LVS from two application VGs, which are from SAN. Below are the steps how i resolved the issue.
For listing and checking the status of available SAN disks (pv-physical volumes). Here, all three disk are visible including vlgroup00 (its is the OS volume)
[root@test3 ]# pvs
PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree
/dev/sda2 VolGroup00 lvm2 a- 29.88G 0
/dev/sdb1 VolBsl lvm2 a- 69.97G 2.72G
/dev/sdc OraEai lvm2 a- 170.00G 1020.00M
Below command lists the existing volume groups (VGs) related each disk. Notice the status “Found exported volume group “ in below output, which means, VGs are not exported. Let us import it by next steps.
[root@test3 ]# vgscan
Reading all physical volumes. This may take a while...
Found exported volume group "OraEai" using metadata type lvm2
Found exported volume group "VolBsl" using metadata type lvm2
Found volume group "VolGroup00" using metadata type lvm2
Now let us import it.
[root@test3 ]# vgimport OraEai
Volume group "OraEai" successfully imported
[root@sdl003 mapper]# vgimport VolBsl
Volume group "VolBsl" successfully imported
Volumes are imported. see the status below.
[root@test3 ]# vgscan
Reading all physical volumes. This may take a while...
Found volume group "OraEai" using metadata type lvm2
Found volume group "VolBsl" using metadata type lvm2
Found volume group "VolGroup00" using metadata type lvm2
Now let us see the status of logical volumes (LVs) all the volume from above two VGs are inactive. For mounting a volume, it must be ACTIVE status.
[root@test3 ]# lvscan
inactive '/dev/OraEai/LvOracle' [10.00 GB] inherit
inactive '/dev/OraEai/LvOraEai' [149.00 GB] inherit
inactive '/dev/OraEai/LvOraArchive' [10.00 GB] inherit
inactive '/dev/VolBsl/LogVol02' [48.81 GB] inherit
inactive '/dev/VolBsl/LogVol00' [4.53 GB] inherit
inactive '/dev/VolBsl/LogVol01' [3.91 GB] inherit
inactive '/dev/VolBsl/home_wbimbprd' [5.00 GB] inherit
inactive '/dev/VolBsl/var_mqsi' [5.00 GB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00' [25.97 GB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol01' [3.91 GB] inherit
Let us activate all volume using lvchange -ay lvname. Here is the single command loop to do the same for all inactive LVs .
[root@test3 ]# for i in `lvscan|grep inactive|awk -F\' {'print $2'}`; do lvchange -ay $i; done
[root@test3 ]# lvscan
ACTIVE '/dev/OraEai/LvOracle' [10.00 GB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/OraEai/LvOraEai' [149.00 GB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/OraEai/LvOraArchive' [10.00 GB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/VolBsl/LogVol02' [48.81 GB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/VolBsl/LogVol00' [4.53 GB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/VolBsl/LogVol01' [3.91 GB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/VolBsl/home_wbimbprd' [5.00 GB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/VolBsl/var_mqsi' [5.00 GB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00' [25.97 GB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol01' [3.91 GB] inherit
Great…, Now I am able to mount the volume..
[root@test3 ]# mount /dev/mapper/OraEai-LvOraArchive /oracle/eaitest/archive
Tuesday, 19 October 2010
Importing and exporting zpool
Here, we use two systems ( white and black) as source and destination hosts.
root@white # zpool create -f testpool /dev/dsk/c4t6005076305FFC08C000000000000100Ad0 /dev/dsk/c4t6005076305FFC08C000000000000100Bd0 /dev/dsk/c4t6005076305FFC08C0000000000001012d0 /dev/dsk/c4t6005076305FFC08C0000000000001013d0 /dev/dsk/c4t6005076305FFC08C0000000000001014d0
root@white # df .
Filesystem size used avail capacity Mounted on
testpool/testfs 9.8G 24K 9.8G 1% /testpool/testfs
root@white # mkfile 9G testfile
root@white # df -h|grep testpool
testpool 9.8G 25K 782M 1% /testpool
testpool/testfs 9.8G 9.0G 782M 93% /testpool/testfs
1. To list all the importable zpool and corresponding statutes apply below command.
root@black #zpool import
pool: testpool
id: 15485920734056515199
state: ONLINE
action: The pool can be imported using its name or numeric identifier.
config:
testpool ONLINE
c4t6005076305FFC08C000000000000100Ad0 ONLINE
c4t6005076305FFC08C000000000000100Bd0 ONLINE
c4t6005076305FFC08C0000000000001012d0 ONLINE
c4t6005076305FFC08C0000000000001013d0 ONLINE
c4t6005076305FFC08C0000000000001014d0 ONLINE
Above output shows that, all the disks related to test pool is available and it can be imported.
testpool 9.8G 25K 782M 1% /testpool
testpool/testfs 9.8G 9.0G 782M 93% /testpool/testfs
root@white # df -h|grep testpool
testpool1 9.8G 25K 782M 1% /testpool1
testpool1/testfs 9.8G 9.0G 782M 93% /testpool1/testfs
pool: testpool1
id: 15485920734056515199
state: ONLINE (DESTROYED)
action: The pool can be imported using its name or numeric identifier.
The pool was destroyed, but can be imported using the '-Df' flags.
config:
testpool1 ONLINE
c4t6005076305FFC08C000000000000100Ad0 ONLINE
c4t6005076305FFC08C000000000000100Bd0 ONLINE
c4t6005076305FFC08C0000000000001012d0 ONLINE
c4t6005076305FFC08C0000000000001013d0 ONLINE
c4t6005076305FFC08C0000000000001014d0 ONLINE
root@white # df -h|grep testpool
testpool1 9.8G 25K 782M 1% /testpool1
testpool1/testfs 9.8G 9.0G 782M 93% /testpool1/testfs
Monday, 16 August 2010
Solaris zfs raw device
The list of available zpool.
bash-3.00# zpool list
NAME SIZE USED AVAIL CAP HEALTH ALTROOT
dbpool 19.9G 1.32G 18.6G 6% ONLINE -
Creating a test volume of 10MB. (Notice the -V option with zfs command, which create a tree for corresponding device under /dev/zvol. This is option is required only when you want to appear this device under /dev/zvol)
bash-3.00# zfs create -V 10M dbpool/test
Creating UFS file system for the created device
bash-3.00# newfs /dev/zvol/rdsk/dbpool/test
newfs: construct a new file system /dev/zvol/rdsk/dbpool/test: (y/n)? y
Warning: 4130 sector(s) in last cylinder unallocated
/dev/zvol/rdsk/dbpool/test: 20446 sectors in 4 cylinders of 48 tracks, 128 sectors
10.0MB in 1 cyl groups (14 c/g, 42.00MB/g, 20160 i/g)
super-block backups (for fsck -F ufs -o b=#) at:
32,
Now the newly created zfs volume is available in below list
bash-3.00# zfs list
NAME USED AVAIL REFER MOUNTPOINT
dbpool 1.33G 18.2G 21K legacy
dbpool/apps 24K 10.0G 24K /app
dbpool/lotus 1.32G 18.2G 1.32G /opt/lotus
dbpool/notesdata 21K 18.2G 21K /notesdata
dbpool/noteslogs 21K 18.2G 21K /noteslogs
dbpool/test 10M 18.2G 24K -
Its ready to mount it now.
bash-3.00# mount /dev/zvol/dsk/dbpool/test /mnt
bash-3.00# df -h |grep dbpool
dbpool/lotus 20G 1.3G 18G 7% /opt/lotus
dbpool/notesdata 20G 21K 18G 1% /notesdata
dbpool/noteslogs 20G 21K 18G 1% /noteslogs
dbpool/apps 10G 24K 10G 1% /app
/dev/zvol/dsk/dbpool/test 7.5M 1.0M 5.7M 16% /mnt
Below is the path for zfs raw device and block device.
Block Device=/dev/zvol/dsk/dbpool/test
Raw Device=/dev/zvol/rdsk/dbpool/test
Ref:
Monday, 9 August 2010
WebDav configuration with apache webserver
Web-based Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV) is a set of methods based on the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) that facilitates collaboration between users in editing and managing documents and files stored on World Wide Web servers.
The WebDAV protocol makes the Web a readable and writable medium. It provides a framework for users to create, change and move documents on a server (typically a web server or "web share").
Appache configuration for webdev:
1. Make sure mod_dav_fs is loaded with Apache
[root@shimna ]# apachectl -t -D DUMP_MODULES|grep dav_fs_module
dav_fs_module (shared)
Syntax OK
The above command list all the modules loaded by Apache and grep fordav_fs_module.
2. Create a lock file with httpd user permission because DAVLockDB that can be written by the web server process
To find out httpd user name group name, grep for User and Group in httpd.conf as below. Here the username is apache and group name is apache.
[root@shimna]# egrep 'User |Group ' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf|grep -v ^#
User apache
Group apache
Now this we can create the lock file.
#mkdir /var/lib/dav/
#touch /var/lib/dav/lockdb
#chown -R apache:apache /var/lib/dav/
3. Create a Apache password file for authentication purpose. Below is the steps to add a user latheefp.
[root@shimna dav]# htpasswd -c /etc/httpasswd latheefp
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user latheefp
4.Editing Apache configuration file
This is the default line in configuration file regarding webdav.
# Location of the WebDAV lock database.
DAVLockDB /var/lib/dav/lockdb
We have to edit above depends up on our configuration like below.
<IfModule mod_dav_fs.c>
# Location of the WebDAV lock database.
DAVLockDB /var/lib/dav/lockdb
#setting an alias path to /locker/audit/web as /webdav
Alias /webdav /locker/audit/web/
<Directory /locker/audit/web/>
DAV On
<Limit PUT POST DELETE PROPFIND PROPPATCH MKCol COPY MOVE LOCK UNLOCK>
AuthName "Webdev for unixindia"
AuthType basic
#Rplace below lines accordingly
AuthUserFile /etc/httpasswd
require user latheefp
</Limit>
</Directory>
</IfModule>
5. Restart Apache
[root@shimna ]# /etc/init.d/httpd restart
Stopping httpd: [ OK ]
Starting httpd [ OK ]
We have completed all required settings in Server side. Now let us see how to access it from Windows system.
Click on Add a network place
Click Next
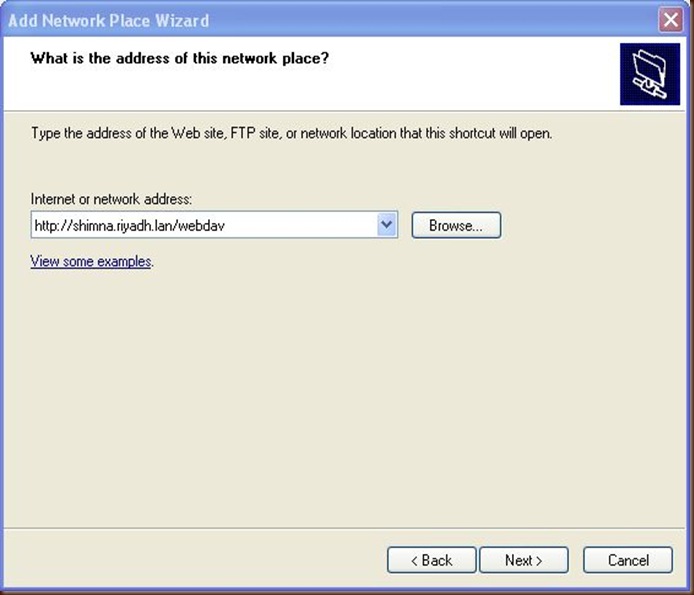
Click on Choose Another Network location
Type the path to webdav directory as above and click next.
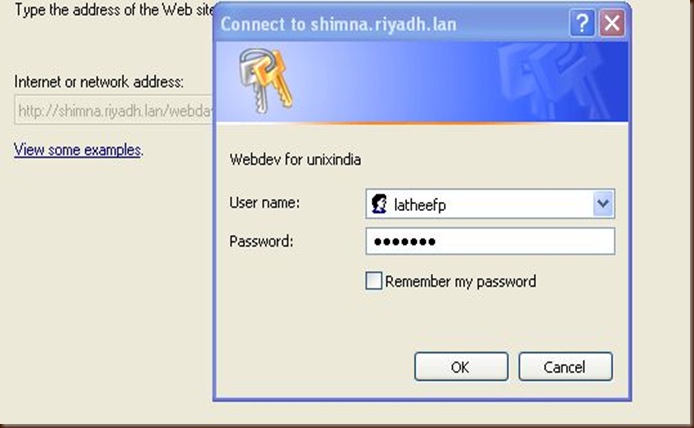
Provide the username and password (here its latheefp and password created using htpasswd command in server configuration)
Just follow above 3 steps. Provide the same username and password when you open the webdav as windows drive for the first time.
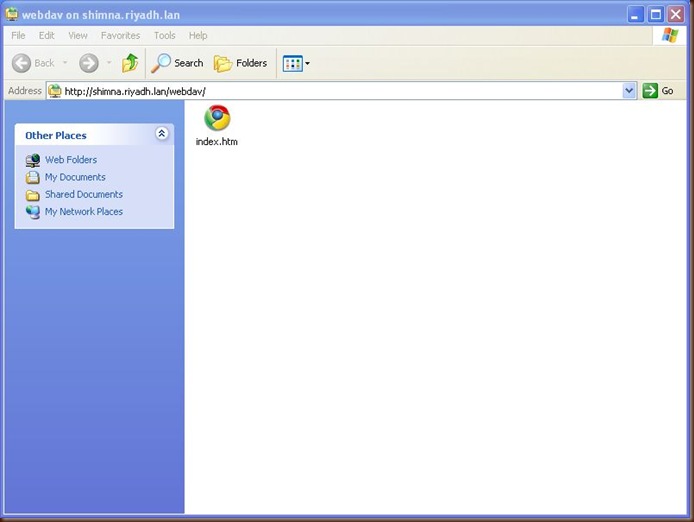
Now the remote wedav is ready to accces as windows directory.
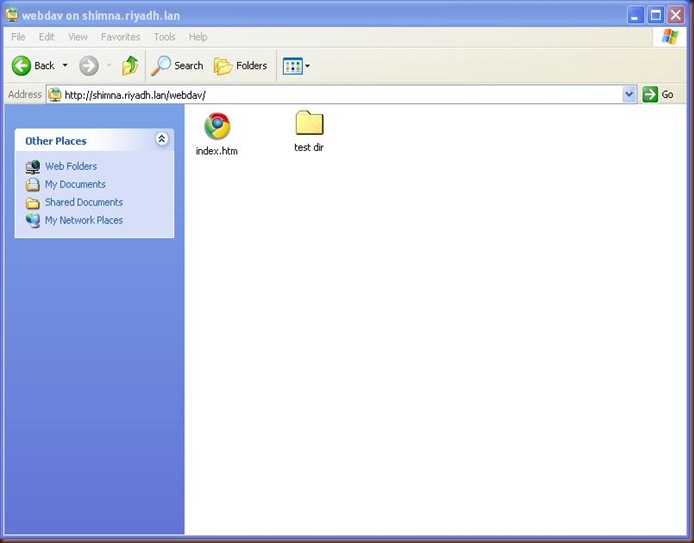
Just created a test dir.